
Effects of temozolomide (TMZ) on the expression and interaction of heat shock proteins (HSPs) and DNA repair proteins in human malignant glioma cells. 2007 252:131–46.Ĭastro GN, Cayado-Gutiérrez N, Zoppino FC, Fanelli MA, Cuello-Carrión FD, Sottile M, et al. Hsp27, Hsp70 and mismatch repair proteins hMLH1 and hMSH2 expression in peripheral blood lymphocytes from healthy subjects and cancer patients. Nadin SB, Vargas-Roig LM, Drago G, Ibarra J, Ciocca DR. Endoplasmic reticulum stress, genome damage, and cancer.
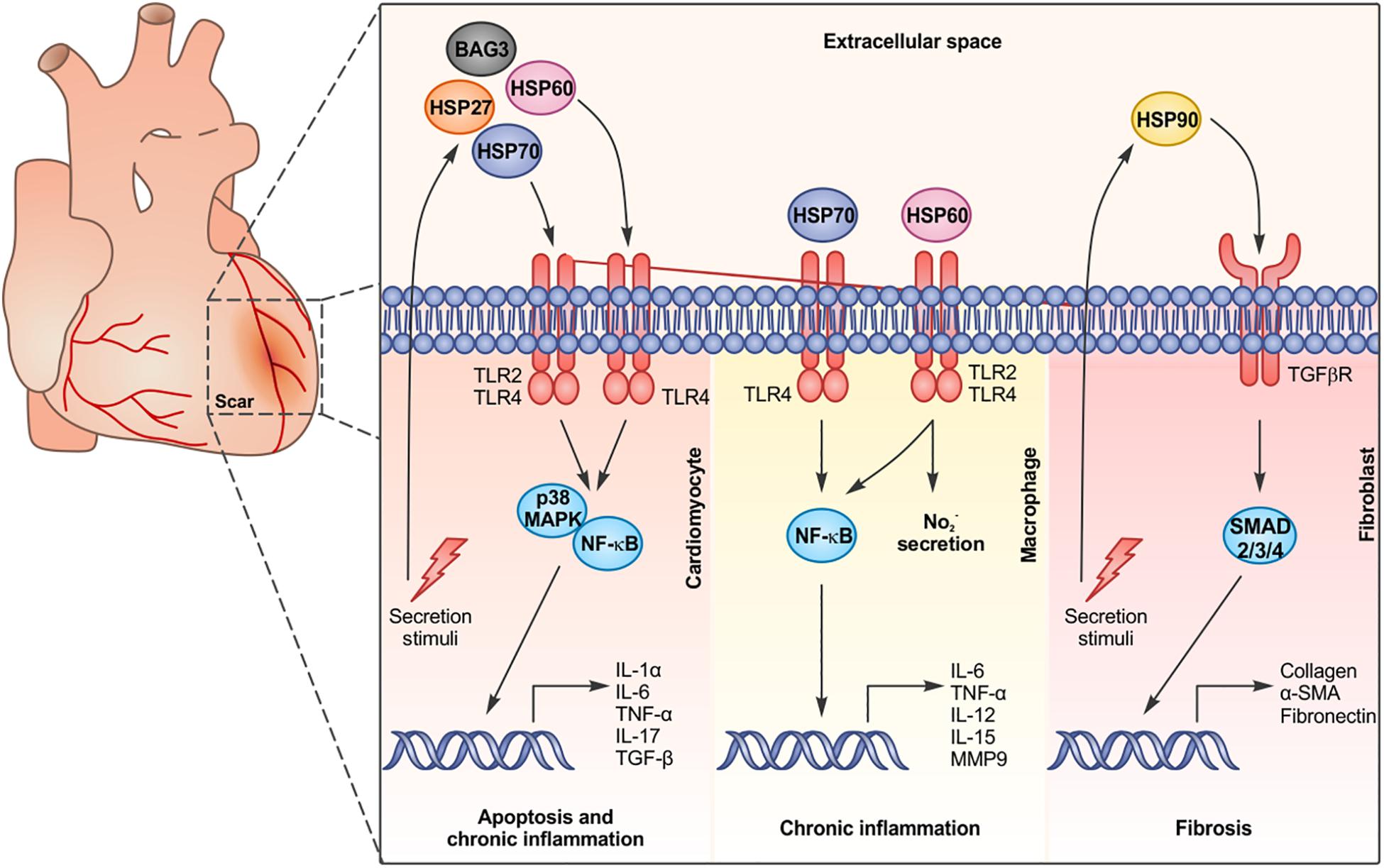
2019 79:2923–32.ĭicks N, Gutierrez K, Michalak M, Bordignon V, Agellon LB. Activation of the unfolded protein response via inhibition of protein disulfide isomerase decreases the capacity for DNA repair to sensitize glioblastoma to radiotherapy. Liu Y, Ji W, Shergalis A, Xu J, Delaney AM, Calcaterra A, et al. ER stress in temozolomide-treated glioblastomas interferes with DNA repair and induces apoptosis. ER stress suppresses DNA double-strand break repair and sensitizes tumor cells to ionizing radiation by stimulating proteasomal degradation of Rad51. Yamamori T, Meike S, Nagane M, Yasui H, Inanami O. Heat shock proteins and DNA repair mechanisms: an updated overview. Repair of DNA double-strand breaks by mammalian alternative end-joining pathways. Homologous recombination and the repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Nonhomologous DNA end-joining for repair of DNA double-strand breaks. How cells ensure correct repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Nucleotide excision repair in eukaryotes. Base excision repair: a critical player in many games. Base excision repair of oxidative DNA damage: from mechanism to disease. Whitaker AM, Schaich MA, Smith MR, Flynn TS, Freudenthal BD. ATM, ATR, and DNA-PK: the trinity at the heart of the DNA damage response. The IXth CSSI international symposium on heat shock proteins in biology and medicine: stress responses in health and disease: Alexandria old town, Alexandria, Virginia, November 10-13, 2018. 2013 332:275–85.Ĭalderwood SK, Repasky EA, Neckers L, Hightower LE. Jego G, Hazoumé A, Seigneuric R, Garrido C. This review aims to present the role of HSPs in DNA repair signaling pathways. Although the role of HSPs in proteins homeostasis and cell death, especially apoptosis has been widely reported, much less is known about their function in DNA repair. DNA damage activates a coordinated response that includes detecting DNA lesions before their transmission to daughter cells, blocking cell cycle progression and DNA replication and repairing the damage. Thus, the ability of cells to repair DNA damage is essential for preserving cell integrity. DNA damage can dramatically alter cell behavior and contribute to a number of diseases including developmental defects, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancer. Most HSPs are rapidly overexpressed in response to cellular injuries including genotoxic stress. They protect intracellular proteins from misfolding or aggregation, inhibit cell death signaling cascades and preserve the intracellular signaling pathways that are essential for cell survival. The molecular chaperones of the heat-shock protein (HSP) family are critical effectors of this adaptive response. In order to ensure tissue integrity and function, cells cope with cellular injuries by adapting their metabolism, protecting essential intracellular constituents, inhibiting cell death signaling pathways and activating those devoted to damage repair. Cells are repeatedly exposed to environmental or endogenous stresses that can alter normal cell behavior and increase cell vulnerability.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
